Football, like most other sports, often heavily depends on a few key moments over the course of the match. When a match-winning or even championship-winning moment is to be decided, the players, coaches, and fans all look to the officials. With Football and events like the World Cup increasing substantially in their viewership, it only means there will be more eyes on the referees every time a decision is to be made. This is normally a place for contention, regardless of whether the final decision reached is correct.
To avoid leaving it to the eye line of the four officials that are on the pitch, FIFA introduced a few more referees in most of the big leagues that would monitor footage from a designated room to increase the accuracy of decisions. However, video assistance referees (VAR) did not go down well with the majority of football fans. This is mainly because, despite the extra attention given to the main decisions, it still saw many choices made by the referees still being incorrect.
This is also further problematic because of the time that is taken to make these decisions. The famed ex-Arsenal manager Arsene Wenger said that the average VAR decision takes about seventy seconds, while it can take much longer if the pitch referee must go to the screen to make the decision himself. In a sport that is reliant on momentum, taking more than a minute to stop the game gives opposition teams time to recoup and catch their breath. This also allows managers to hand out instructions to counteract previous shortcomings. That means that the time taken for the referees to decide took away or presented an advantage that did not exist before, ruining the flow of the game.

There have been qualms against the way refereeing is carried out for a long time. While it is unlikely that these reservations will ever be quelled, VAR has proved not to be the solution that will improve the game. As a result, FIFA has proposed a plan for a new ‘semi-automated’ offside technology to combat the shortcomings of VAR with respect to the offside rule, specifically.
Read More: Five Personal Finance Startups that are Revolutionizing Fintech
What is the Offside Rule?
To understand whether this innovative technology will be effective in improving the game, one must first grasp the concept of the complicated ‘offside rule.’ The offside rule was designed to avoid attacking players influencing the game while being behind the last defender on the opposition team. This meant that defenders had more flexibility in their tactics and could decide whether they wanted to keep a high line or not. This also meant attackers could not simply wait at the offensive end of the field for a pass to come in.
While the rule is quite nuanced and well explained on the British Football Association’s website, it stipulates that a player is in an offside position if he/she has any part of their body closer to the opponent’s goal line than the second-last opposition player.

However, this is only penalized when they influence the flow of the game. This occurs in two main ways. The first, and more obvious, is when a player tries to pass the ball to their teammate who is in an offside position. If the player receiving the ball is in an offside position when the ball is released from the passing player, the play is then voided, and a free kick is awarded to the opposition team. Therefore, it is exceedingly difficult to time runs as an offensive player.
The second way an offside offense can occur is if the player that is in an offside position influences the defending team’s actions when an attack is mounted. For example, if a player obstructs the view of a goalkeeper and influences the result, it is an offside offense (even if the player did not touch the ball).
Read More: Sustainability in Tech: 3 Ways for Companies to Become More Sustainable
New Horizons for Offsides
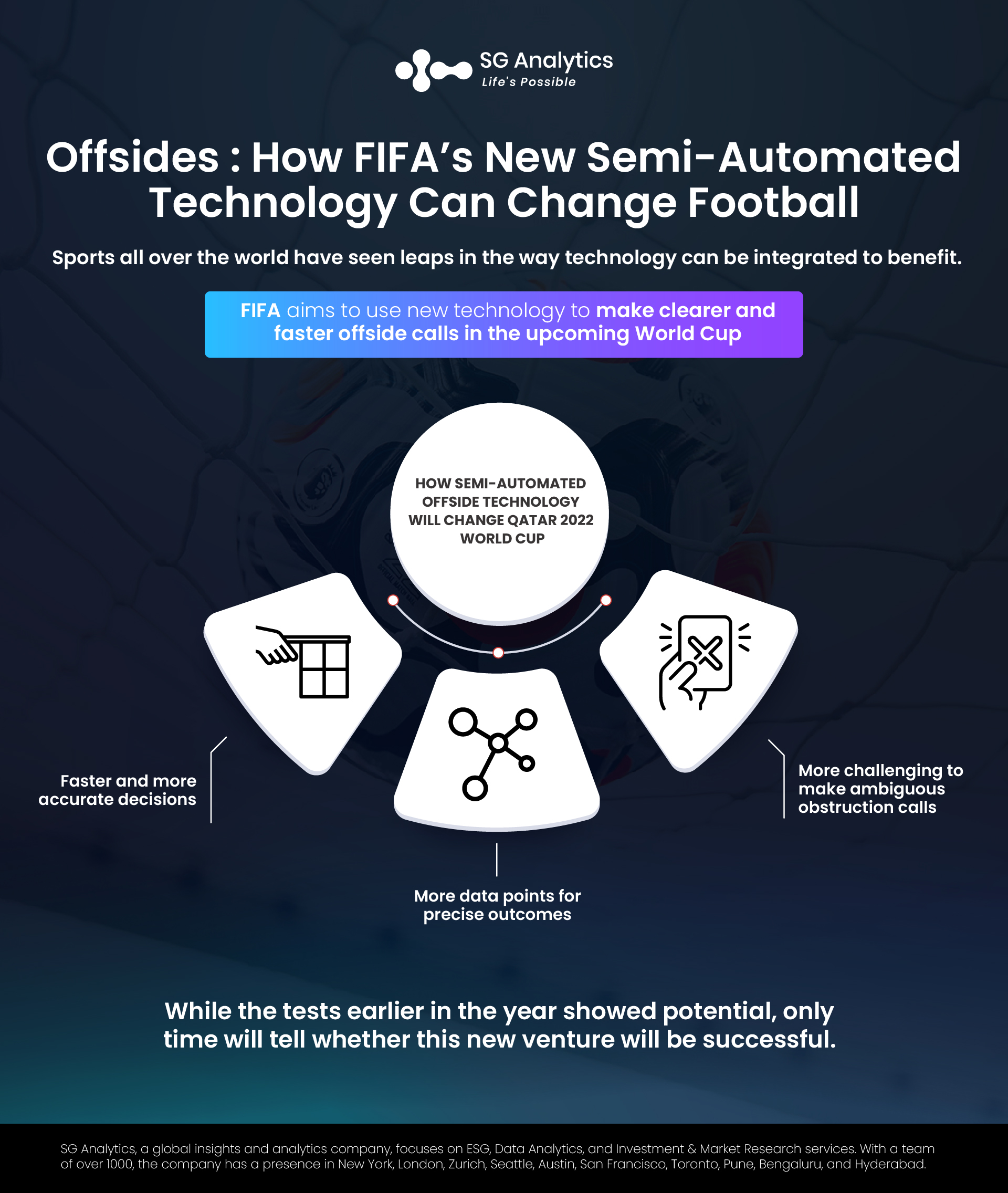
Naturally, offside decisions tend to be a contentious part of football and refereeing. As the difference between a goal and an offside call can be mere centimeters, fans often disagree with the official’s decision. The new technology aims to add more accuracy to that. All the world cup stadiums will be equipped with 10-12 specialist cameras that will use ‘limb-tracking’ technology to map twenty-nine points on each player’s body. Each of these points will relay its positions to the system about fifty times every second to ensure the highest level of accuracy for split-second decisions. All this information is combined with image-processing algorithms to give the video assistant referees a perfectly accurate view of whether the player was offside or not.

The process is still considered semi-automated because it requires the video assistant referees to discern the offside based on the data provided. Despite this, the place for human error is alleviated, if not virtually eliminated. Furthermore, all this data is compiled in real-time, meaning that the officials in the video room can see a recreation of the play in mere seconds to determine a call. This helps in avoiding the disruption of momentum as decisions are made much faster, and there is little stoppage to be made for an offside check.
Another issue with the current offside call method is that fans are unable to see clear images of whether a player is offside because of the inaccurate line drawing technique that they have used in the past. The modern technology will be paired with basic animation models to create a visual depiction of the play so that fans, too, can see how or why a player was flagged offside. These animations will be like that of the goal line technology, which has gone down well with football fans worldwide and has become a staple of Europe’s top five leagues.

Drawbacks of the New System
The recent technology being implemented seems like a big step in the right direction for refereeing. For years, the sport has seen advancements while the judging process for the offside rule remained antiquated and frequently inaccurate in crucial moments. When a match is defined by these small moments, it is clear that this was an important problem that needed to be combated at the soonest. However, it is also clear that this new solution will also come with its own shortcomings.
The first and main shortcoming of the new semi-automated technology is the fact that it is only activated when there is contact made with the ball. When a player is offside, the referee will see their watches light up red within seconds of the play being made. However, this is only when a pass is made to a player who was in an offside position. This means that the players who are in offside positions and are obstructed by players/the goalkeeper or influencing the game in other ways are more difficult to account for.
The second shortcoming, in tandem with the first, is that the more ambiguous decisions still need to be made by human referees. When it is an issue of obstruction or influencing, referees must also take the time to ensure that the decision must be made. This takes away from the new technology’s ability to reduce decision times.
Read More: Minimizing Financial Risk With Corporate Governance
A Step in the Right Direction
This new solution is pegged to be a game changer for referees and the sport. While it seems as though these innovative technologies will be expensive, and we are only likely to see them in the more prominent and well-funded leagues in the next few years, it is a substantial change to improve the way the sport is officiated.
Bearing that in mind, it is also clear that this is far from a proverbial silver bullet as it remains clear that this technology has a long way to go before the refereeing is perfectly accurate. FIFA has made it clear that they want to improve the way fans perceive the officials, and that is a critical step towards that. Avoiding contention and making decisions less ambiguous is the best way to foster trust between all parties involved.
It might be unrealistic to strive for perfection when it comes to refereeing in football. Some might even argue that the possibility of incorrect decision-making adds a certain air of jeopardy and excitement to the sport. However, these new innovations will improve the way the sport is played and viewed, making it a more seamless experience for everyone.
With a presence in New York, San Francisco, Austin, Seattle, Toronto, London, Zurich, Pune, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad, SG Analytics, a pioneer in Research and Analytics, offers tailor-made services to enterprises worldwide.
A leader in Market Research services, SG Analytics enables organizations to achieve actionable insights into products, technology, customers, competition, and the marketplace to make insight-driven decisions. Contact us today if you are an enterprise looking to make critical data-driven decisions to prompt accelerated growth and breakthrough performance.