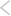Artificial intelligence has come a long way in the last few years. While it was initially used mostly for analytical work, the dawn of generative AI is opening up a whole new wave of use cases for AI. Simply put, generative AI is the technology to create new content by utilizing existing text, audio files, or images by using data-intensive AI capabilities like deep learning and neural networks. With improvements in model and computational power and the availability of more data, AI is now able to recognize underlying patterns from a vast collection of digital sources to come up with the required output.
.jpg)
What’s New?
AI technology has become incrementally better since its inception. The quality of generative AI output has now come to the point that is meaningfully good for creators and businesses. For instance, before 2020, the majority of use cases of AI (or rather traditional AI) were in spam detection and translation. That has changed now. More and more creators and marketers are using generative AI outputs for writing emails and promotional blogs. For writing that requires more creativity, generative AI outputs are already being used as first drafts, which for the time being, require further refinement. Leading US-based VC firm Sequoia Capital estimates that as the generative AI models are further improved, the technology will be able to write final drafts as good as if not better than, professional writers by 2030.
Read more: Tech-Related Ethical Concerns Businesses Should Address in 2022
Fig 1: AI Models Keep Getting Better

Source: Sequoia Capital
Another reason why generative AI is the buzzword these days is the proliferation of open-source alternatives. For instance, Eleuther.ai’s GPT-NeoX-20B is an open-source alternative to OpenAI’s GPT-3 model for text generation and StabilityAI’s recently launched Stable Diffusion is the open-source alternative to OpenAI’s DALL-E 2 for images and videos. By democratizing AI, these open-source alternatives are making AI easily accessible and affordable. Some estimates even suggest a 100x drop in the last two months in the cost to generate images and a 10x drop in friction to generate output in the last six months.
Burgeoning Use-Cases
With AI models undergoing transformation changes, the use cases have expanded significantly, particularly in creative industries. Applications of generative AI in the advertising and marketing industry are huge and wide. Companies including Copy AI, Jasper, Copysmith, and Contenda are pioneers in copywriting.
Read more: Global Business Trends Outlook 2023
Fig 2: Generative AI Application Landscape
Source: Sequoia Capital
Additionally, generative AI has use cases in coding as well, with companies like GitHub, Debuild, Mutable AI, and Moderne working on solutions like code generation, web app builders, and code documentation. While current tools help developers work faster and more efficiently, giving consumers access to code could bring in a new customer base and expand the addressable market significantly.
Read more: The Next Tech Time Warp: How Will Artificial Intelligence Possibly Change the World?
More applications of generative AI lie in design, gaming, and social media. Typically, design prototype development for digital products is labor intensive. Generative AI start-ups can solve this issue, especially when there is labor constraint. In social media, generative AI start-ups can create new social experiences. Further, generative AI for chatbots has been gaining traction for a few years now.
The rapidly expanding adoption of these generative AI start-ups is also reflected in their growing numbers. For instance, OpenAI’s image generator DALL-E 2 has more than 1.5 million users, while Mid journey has 3+ million users on its official Discord server. Remarkably, Mid journey entered open beta in July 2022. In its first full year of business, Jasper has registered $35 million in revenue and aims to attain yearly revenue of $75 million by the end of 2022.
Read more: Forecast: Top Venture Capital Market Trends In 2023
VCs Eye Opportunity
Some investors are likening generative AI to the early days of the web, seeing it as a transformative platform shift. US-based VC firm Sequoia sees generative AI as a technology that could generate trillions of dollars of economic value. As the demand for AI-powered content generation accelerates, generative AI start-ups have been garnering significant VC attention despite a broader slowdown in the pace of VC funding. Jasper, an Austin-based start-up, recently raised $125 million in Series A funding at a $1.5 billion valuation. London-based Stability AI also raised $101 million in an oversubscribed round, with investors like Coatue and Lightspeed Venture Partners participating. In May, Hugging Face also raised $100 million in a Series C round at a valuation of $2 billion.

The backing from big is another stamp of approval for generative AI start-ups. Microsoft has made significant investments in OpenAI and is anticipated to enhance its OpenAI efforts this year. Additionally, Google and Meta developed a new artificial intelligence tool to produce a video from a simple text prompt. Such interest from big tech could also very well spark a wave of M&A in the generative AI space.
Even if generative AI output can’t yet match the human-generated output, businesses and creators see them as handy tools in a broader toolbox. Further, a large number of firms are using generative AI to improve efficiencies and speed in their operations, providing value for their customers. That said, businesses need to address ethical concerns, which are often associated with AI.
With a presence in New York, San Francisco, Austin, Seattle, Toronto, London, Zurich, Pune, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad, SG Analytics, a pioneer in Research and Analytics, offers tailor-made services to enterprises worldwide.
A leader in the Technology domain, SG Analytics partners with global technology enterprises across market research and scalable analytics. Contact us today if you are in search of combining market research, analytics, and technology capabilities to design compelling business outcomes driven by technology.