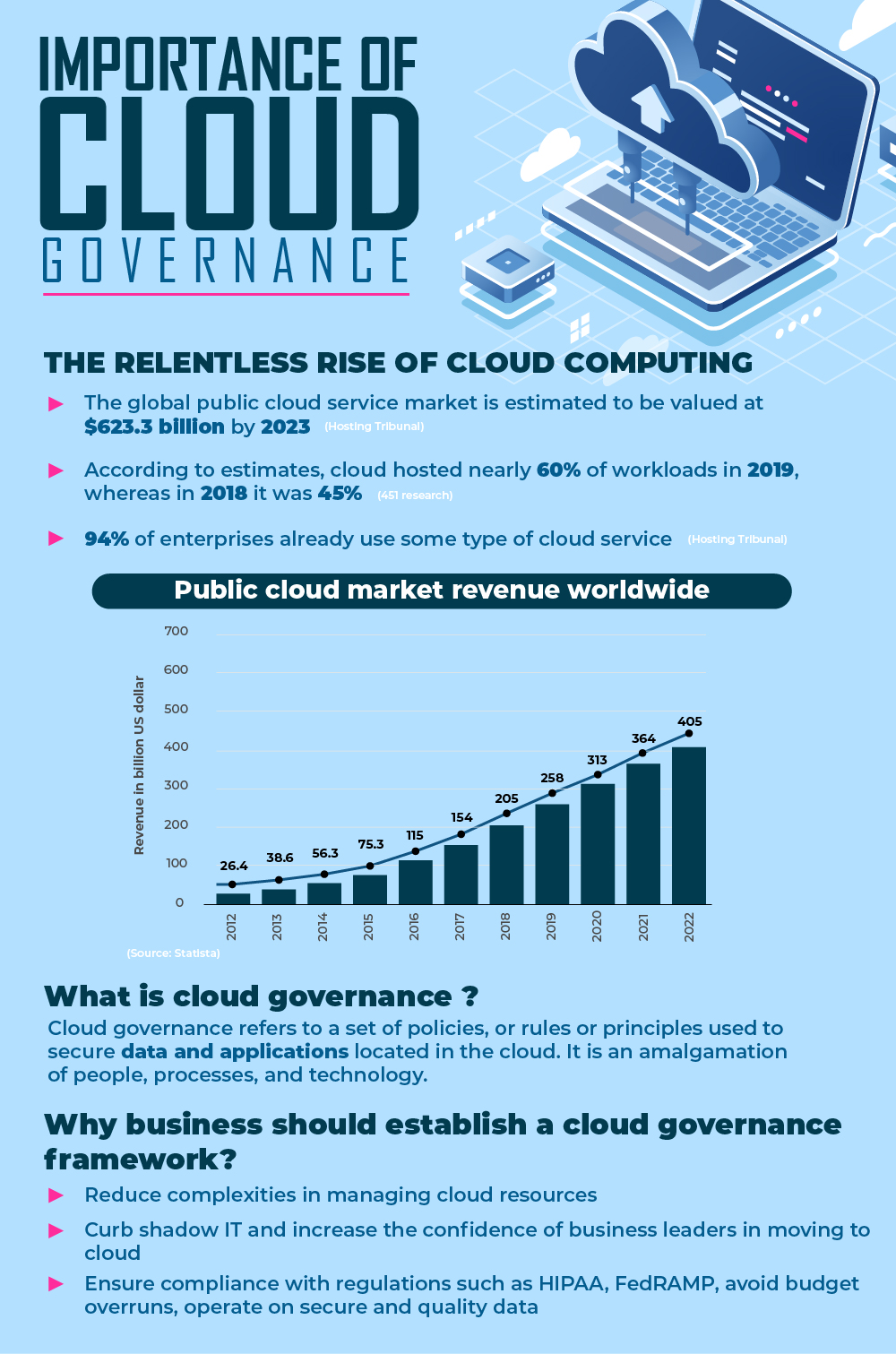
According to estimates, cloud hosted nearly 60% of workloads in 2019, whereas in 2018 it was 45% (451 research). The relevance of cloud computing has grown vastly in recent years as companies are embracing digital transformation actively to thrive in the digital age. The global public cloud service market is estimated to be valued at $623.3 billion by 2023 (HostingTribunal). Cloud governanceis the outcome of the active adoption of cloud computing by enterprises.

What is cloud governance?
Governance is basically a set of agreed-upon policies and standards that helps in implementing a program/process effectively and making stringent decisions. Cloud governance refers to a set of policies, rules or principles used to secure data and applications located in the cloud. Cloud governance is an amalgamation of people, processes, and technology.
In simple terms, cloud governance comprises process, policy, and criteria for planning, decision making, architecture, operation, deployment, and management of cloud computing services.
Why is it important?
To get a clear perspective, consider companies running their businesses on an on-premises IT infrastructure. These companies have a clear picture of their capital cost and monthly operational expenses. Also, they are aware of the departments that will be running the software/application/program.

However, in the case of the cloud, the building of systems and deploying of assets is just a click away. Though organizations need not worry about capital costs, the operational costs may overrun within a short span. Also, communication between software, programs, or applications deployed by different departments may not be possible. Lack of control leads to cost and efficiency-related issues. With cloud governance issues related to efficiency, cost, labor, and many others can be significantly eliminated.
Below mentioned are some of the use cases that exhibit the relevance of cloud governance as companies are leaning more towards cloud services:
Reduces complexities in managing cloud resources: An extensive and effective governance strategy is essential to gain in-depth visibility around an organization’s cloud activities and keep tabs on trends. By using multiple accounts, organizations can manage definite cloud workloads and can deliver precise access control. This also helps in monitoring and managing operational costs. Also, with a structured cloud governance framework companies can be less worried about security and costs in the case of an unprecedented issue. Even the leading cloud service provider, AWS, advises customers to move multiple-tenant workloads in a single cloud account into distinct accounts.

Helps in curbing shadow IT: The key challenge in operating in the cloud is that the users are clueless about where their data resides, or which system is in use. Therefore, many times users have to use shadow IT to gain access to their resources to complete their work. Cloud governance helps in overcoming this challenge as it provides a framework that enables easy request and frictionless access to cloud resources within the budget and compliance constraints. This not only reduces employee frustration but also avoids the reluctant usage of personal cloud accounts by staff members. Cloud governance also helps in increasing the confidence of business leaders in moving to the cloud.
Reduces risk and labour: Though the cloud is convenient and complements various business activities, the risks that come with exposed data is diabolical. The other factors such as cost overruns, non-compliance with regulations/policies augment the risks and add to the complications in operating in the cloud. With a cloud governance solution, organizations can not only ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA, FedRAMP, etc, but also avoid budget overruns, and operate on secure and quality data.
Additionally, with cloud, companies no longer must rely on spreadsheets and manual efforts and processes to track accounts, cost, and compliance. Instead, they can set up guardrails that will help in controlling access, budgets, and policies for projects and receiving timely alerts. Cloud governance enables labour savings and helps business professionals in focusing more on value-adding and mission-delivering activities.
Building blocks of the cloud governance program
Though governance necessities are directly influenced by an organization’s business objective, some basic principles must be involved in a cloud governance program. Following are the basic principles that form the building blocks of a cloud governance program:
Financial management: Comprises policies related to budgets. Organizations need to keep an eye on the cost trend influencers to optimize their budgets and invest smartly
Cost optimization: With the help of a cost optimization policy, organizations can optimize their spend and ensure that discounts are fully utilized
Operational governance: This includes system testing, identification and termination of ZOMBIE assets, software testing & QA, and scheduling stop/start time for non-production instances that are engaged in development
Performance management: An effective cloud governance model demands asset optimization based on workloads. The performance management principle focuses on downgrading and upgrading assets as per demands. One of the best practices in cloud governance is to ensure that an enterprise’s data is stored in a most cost-effective yet secure location
Asset & configuration management: This principle typically includes everything from consistent tagging for cost allocation to identifying non-conforming assets – those that exceed permitted capacity, incompatible with existing assets, etc.
Security and incident management: This principle aims to accelerate cloud security by applying encryption, access controls, audit trails, security groups, application access rules, etc.
Practical guidelines to establish a cloud governance framework
Today, most organizations, large and small, are already using cloud services and considering new ones before constructing their cloud governance model. 94% of enterprises already use some type of cloud service (HostingTribunal). Also, an organization’s need is greatly driven by technological advancements in current times. Therefore, companies should first assess and determine the project scope, workstream, and timeline for the launch of the governance program.
Following is a set of cloud governance best practices:
- Consider all actors in the cloud platform. Identify and define the roles and responsibilities of the individuals in the governance program
- The organization’s business objective should drive the scope of the governance program. Broaden the scope of the program charter to meet future needs. However, define the project scope precisely and have a step-by-step approach in delivering program elements
- Create open standards for the cloud governance program and ensure that standards are in line with the existing industry standards
- Segment project workstreams to evaluate what is in use and what is not. The workstreams can be combined again once the immediate business needs are met
- Determine standards for monitoring and reporting. Create enterprise-wide alerts to get a comprehensive view of the company’s compliance status
- Set up an enterprise-wide communication cycle while the program is under construction across the organization
- Perform audits and compliance check on deliverables, particularly if the cloud governance program is built to address an existing or known deficiency
- Business and IT stakeholders should try to understand each other’s domains and challenges to make ubiquitous decisions regarding the governance program
Challenges in establishing a cloud governance framework

An enterprise cloud usage is likely to be the new normal for organizations in the upcoming years. Though cloud governance is as promising as the capabilities of cloud computing, establishing a cloud governance framework comes with a set of profound challenges. Following are some of them:
- Organizations are completely unaware of who is accountable for the security for sensitive or confidential information stored in the cloud
- IT is completely sidelined when decisions regarding cloud resources usage are made
- A company’s IT department is not sure if they are fully aware of all the cloud resources used by their company
- Though companies agree that encryption is highly important, not many of them apply it for protecting the apps
- Compliance becomes more complex as organizations cannot merely control how their employees or third parties handle sensitive data
- Most employees use cloud apps without proper security training. This might allow for grave security issues on the cloud
- Third parties can access sensitive data without security reinforcement like multi-factor authentication
Wrapping Up
By 2022, over 1.3 trillion in IT budgets are likely to be affected by the shift to cloud (Gartner). Cloud is creating a massive transformation in the business world and will continue to do so in the years ahead. Bottom line – the future of computing is inevitably in the cloud as it is no longer just convenient and cheaper to boot, but also more mature and reliable. Thus, in the upcoming years, cloud governance will be as inevitable as cloud computing.