While revenue generation and a growing number of storefronts have been an organization’s greatest asset, the digital age has heralded the importance of a more critical asset; data. Today information holds power, and businesses boasting strong data harnessing abilities are likely to stay ahead of industry trends and, more importantly, customer demands.
Recruiting in house professionals can be a resource-consuming undertaking. Companies are more likely to outsource data engineering services to professionals managing similar processes day in and day out. Larger organizations, on the other hand, require quicker results and are more likely to facilitate operations internally. No matter what the chosen method, data engineering is a critical component of business success and must be streamlined for the best possible results.
What is Data Engineering
The digital era has incorporated data into every aspect of our existence. Big data, cloud data, AI training data and personal identification data are all categories of information pertinent not only to us as consumers, but to corporates for better decision making. As a result software engineering has evolved to incorporate a new subdiscipline; data engineering. Data engineering covers the transportation, transformation and storage of information the organization is keen to retain.

Data engineering professionals first identify the goal of performing the service and then piece together the best approach to facilitate the same. The end goal is to ensure organized, consistent data flows through the organization to enable seamless end to end business activities.
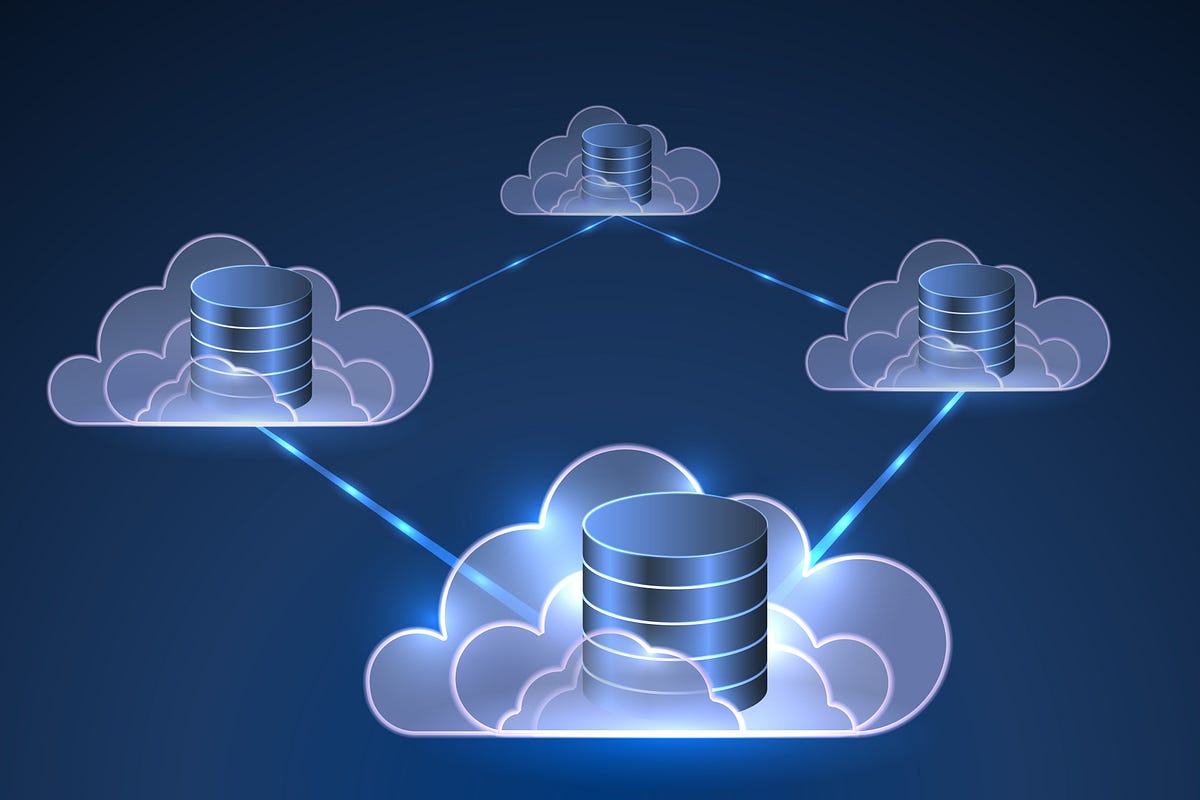
A simplified data pipeline consists of multiple data sources transported to a unified data lake. From the lake, a data model compiles and segregates information and moves the same to the production database for access by employees and other stakeholders. As the information can be captured from a number of sources, including IoT devices, user activity, and vehicle telemetry, introducing a comprehensive data engineering tool is critical to ensuring duplicate or incorrect information is not transported to the production database.
Additionally, a large number of businesses are moving towards building internal data platforms. As having a single pipeline for incoming data may not provide the results needed, large organizations with multiple teams, for instance, need access to different kinds of information. Data engineers are able to craft models with multiple pipelines that address requirements from multiple departments simultaneously.
Data Engineering Trends for 2021
As data engineering plays a larger role in today’s organizations, staying on top of trends within the field offers insight into future business investments and methods to optimize efficiency and effectiveness of the same. Here are six key trends to watch for;
1. Product-Focused Data Engineering Roles
Data engineers are enjoying strong professional demand. Currently, data products serving external demand must be equipped with customizable and scalable options in order to meet multiple demographics and client requirements. While conventionally, data engineers are recruited to build systems that can be reused with various internal clients, there is growing awareness and request for individuals with a data-driven product company background.
These are professionals who craft solutions based on outcome, and customized based on end results rather than just building them based on business requirements. The practicality of these professionals is likely to make them strongly sought after in corporate environments.
2. Data Engineers met DevOps
A growing number of teams are looking to incorporate engineers who are able to not only clean data but build machine learning pipelines and productionizing models. In addition to these requirements, there has been a recent growing demand for professionals who are also adept at DevOps methods.
This allows engineers to effectively test and troubleshoot within a production environment. Conventionally most engineers are equipped with the skillset to conduct the same but have chosen to stick with data engineering work. The increased demand for the application of the skillset has encouraged more engineers to capitalize on all the skills available at their disposal for more comprehensive solution generation.
3. Blurring the Line between Data Scientists and Big Data Engineers
As the concept of a data engineer evolves, businesses are able to find their information management needs within a single professional. Professionals well versed with data engineering are equipped with the skills to handle big data management (including statistics and modelling) are in growing demand, especially within healthcare and medical fields.
It is expected that all professionals within a data engineering field are likely to have some experience dealing with IoT and streaming data.
4. Hybrid Roles
While we have mentioned introducing professionals with a combination of two pertinent data management skills, there is likely to be high future demand for professionals able to encompass all the above-mentioned skills. A single data scientist with the ability to incorporate machine learning, conventional engineering and DevOps practices into one cohesive role is considered a “unicorn” by businesses today but is likely to become a norm moving forward.
The prospects may seem strongly beneficial to an organization. Introducing one professional with an end-to-end solution helps keep activities consistent and creates a one-stop shop for all data related needs. However in practical application finding an individual with professional capabilities across all areas could be misleading and frustrating should things not work as seamlessly as expected.

5. Remote Data Engineering
The ongoing global pandemic has pushed more organizations into encouraging work from home setups. As a result, professional opportunities are no longer geographically bound and allow organizations to hire based on merit and skill, not just what is easy to recruit. This creates stronger opportunities for professionals in the field simultaneously. Reaching new professional opportunities and heights from the comforts of our home has truly never been easier.
6. The movement from On-Premise to the Cloud
It is projected that by 2022, 75% of all databases will be moved to the cloud (Gartner). More organizations have been in the process of moving their operations to virtual environments as is; data engineering moving to a unified digital space can only help businesses conduct activities faster. Only a meagre 5% (BurtchWorks) of businesses are considering maintaining their on-premise solutions. The advantages generated by moving to the cloud include cost and time savings, mobility and enhanced reliability.
Conclusion
In 2004, Gartner conducted a report surveying 600 major enterprises across Australia, The UK and the US. 75% (EDM) of respondents reported issues caused by defective data. If these were concerns cropping up almost two decades ago, the importance of effective data management cannot be denied in today’s day and age.
Data engineering offers businesses the ability to streamline information to create pertinent data for future planning and decision making. Understanding trends within the space and implementing the same where possible can be the difference between an organization succeeding or succumbing to their competitors.